This article provides an overview of the major features available in Resolver Core 2.0, which is expected to released near the end of January, 2018.
User Interface: New Navigation
The new user interface offers a refined hierarchical, top-down structure in its navigation, providing contextual information that helps the user understand not only where they are in an app, but which task or function they should be completing.
By replacing the left navigation menu with a top navigation bar that includes both dropdown menus and tabs, valuable screen space is freed up while simultaneously providing more application/activity-related information as users move around an app.
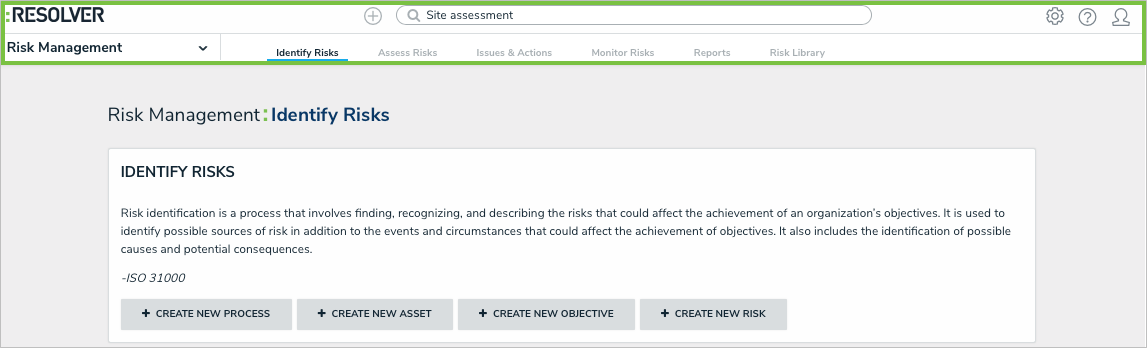
For more detailed information on the new user interface, watch the Resolver Core 2.0 New UI Orientation video below.
Assessments
Assessments are a key building block to Resolver Core as they support multiple business activities across most of the apps. Broadly speaking, an assessment is a point-in-time or continuous evaluation of data in the context of a business activity. Some assessment examples include:
- Risk assessments
- Control assessments
- Control testing
- Security audits
- Audits
- A/B testing
- Scenario modeling
Note: Not all the examples listed above are supported in 2.0.
Additional Data Types
The 2.0 release introduces the concept of reference data, which helps the user understand how the assessed data relates to the bigger picture across the organization. Reference data is important, secondary information within an assessment that does not actually need to be assessed. Potential examples of data that can be used as a reference include:
- Legislations
- Business units
- Locations
- Departments
- Products
- Teams
- Major processes
- Objectives
When an object in an assessment is flagged as reference data, it prevents additional instances of that object from being created at the launch of an assessment, avoiding data bloat while providing better organization of the data.
Assessment Scoping
Users can search, explore, and refine assessment data via the new scoping tool. The ability to explore permissioned data will contribute to more efficiently scoped assessments, draw connections between data across an organization so testing can be done in sync, and easily include past data from previous assessments (e.g. relaunch from a previous quarter, leverage other team’s conclusions).
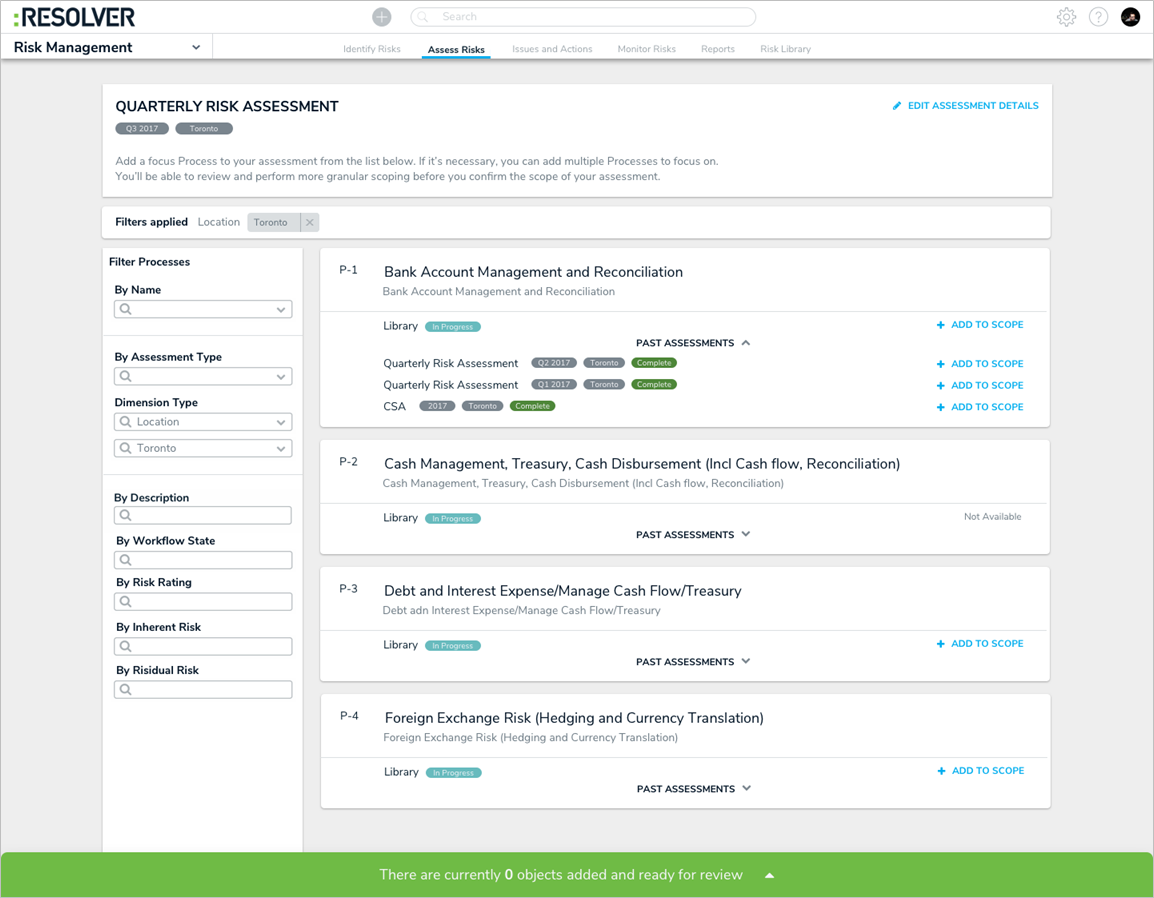
Intuitive Display
Understanding data is critical. Users need the visibility of data across the organization in its current state but also need to understand how that data has been changing over time and across business units. Did this control fail last quarter? How has that risk trended over time? Why? These are just some of the question we need to be answered to accurately make conclusions on the current state.
To do this, 2.0 has introduced the ability to access previous assessment results via fields while assessing objects. This enables all user types to make more confident and accurate conclusions.
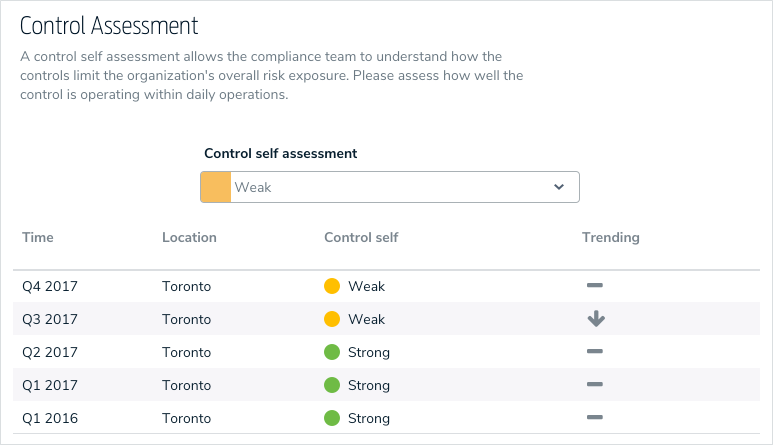
Additionally, intuitive grouping of assessment instances by the originating assessment in search, scoping, and relationships mean that it’s easier to visualize how objects change over time and map the correct instance to applicable objects.
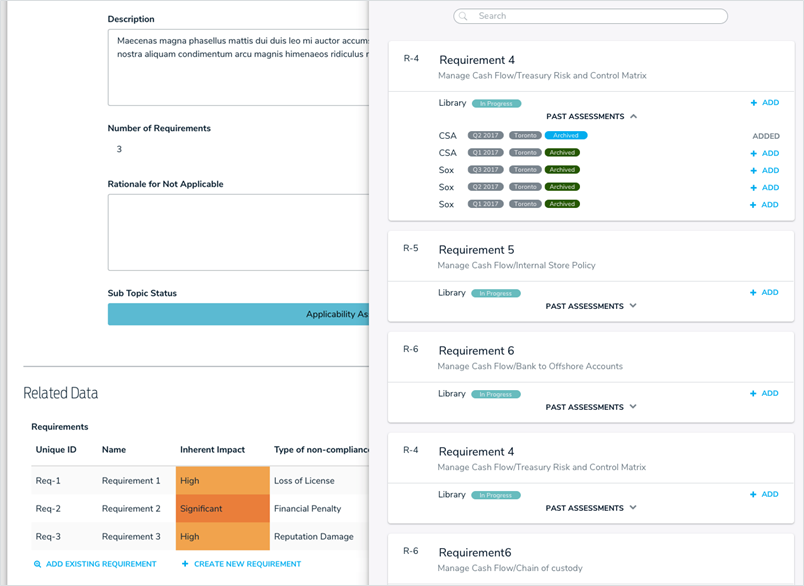
Navigation Form (Tree Browsing)
In previous versions, users didn’t always understand where they were, which objects are related to another, or how to access these related or referenced objects. The new navigation form corrects these issues.
Organizations tend to think of their data in a hierarchical structure and with the navigation form, you can now connect your highly configurable forms or reports to any object. The tree provides context by representing the data in a structure that’s both familiar and easily accessible.
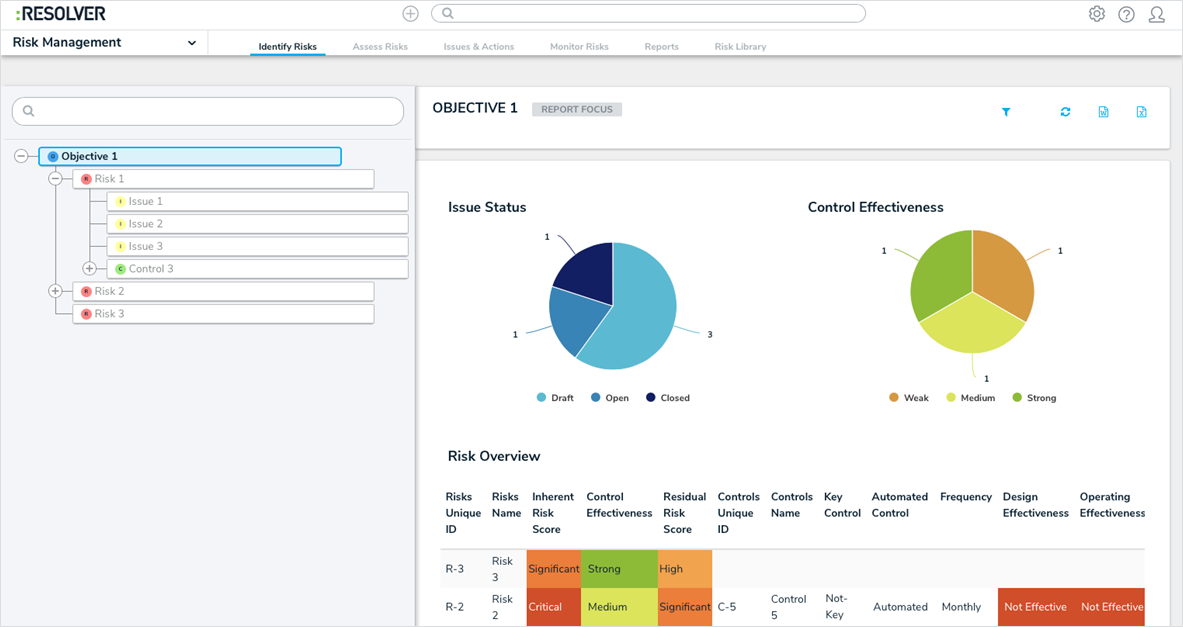
Assessment Workflows
Although the properties and fields of an object (e.g. risk, control, or incident) may be similar, the process these objects go through are typically dependent on the application (e.g. a risk in Security Audit versus ERM) or the assessment (an audit assessment versus a risk assessment). For example, SOX assessments focus on controls and require an extended life cycle that potentially differs from an audit assessment, it requires more coordination and involvement from multiple resources.
Assessment workflows enable this flexibility by allowing administrators to tailor an object’s workflow at the assessment level, allowing you to create different workflows for the same objects across multiple applications and assessments.
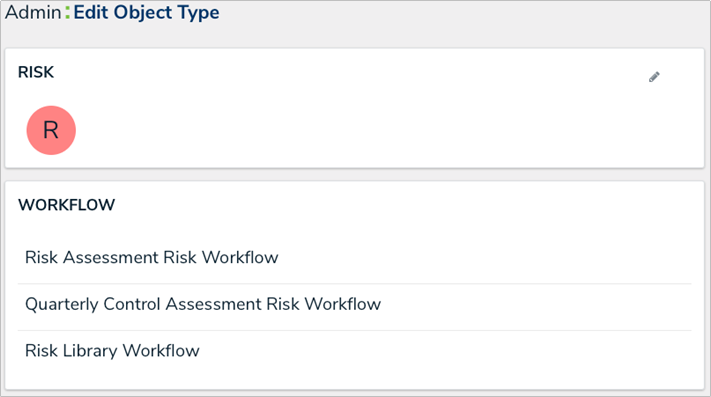
Workflows
Orchestration
Orchestration enables communication between objects. Objects can “talk” to and “instruct” each other, which dictates behaviors based on actions or assessments taken on another object. In other words, using orchestration, changes to one object can force a change to a related object. Events that could benefit from orchestration include:
- Kickoffs
- Escalations
- Close Audits
- Launch a Risk Assessment
- Launch a Control Assessment
More specific examples include:
- Close an Audit: Clicking the Close button at the audit level closes all open issues and marks all tests as Complete.
- Launch a Risk Assessment: Sets all processes, risks, and controls from Draft to In Progress. All objects transition, the objects are time stamped with start dates (a new workflow action feature), and emails are sent to the appropriate owners.
Workflow Actions
Expanding on the above, the new workflow actions add another level of automation to an organization’s processes, providing less hands-on work and more standardization of data changes.
These new actions include:
- Clear Fields, Role, or Relationships (e.g. clear roles when launching an audit. Clear fields, issues, and action plans when reassessing controls, risks, or processes).
- Set Date fields (e.g. extension requests or time stamping start or completion dates). As assessments progress, dates need to be responsive as the objects move through different stages. Workflow date actions will enable:
- Time stamps (e.g. the start or completion of an assessment).
- Deadline setting (set a date two weeks from today).
- Extension deadline (e.g. request extension. If approved, reset the deadline date today, but add 5 additional days).
State Categories
State categories will help users understand completion percentages and segregate data across the applications. For example, Library versus Assessment versus Archived data.
This feature will continue to evolve in future releases. More to come…
Additional Features
Filters
Date-based filters can now be applied to reports. This feature is useful for situations such as running reports on issues created in the last month or action plans that have been opened in the last week.
Field Type: URLs
The URL field type on forms enables users to upload files, files and links, or links only.